By: Denise Simon | Founders Code
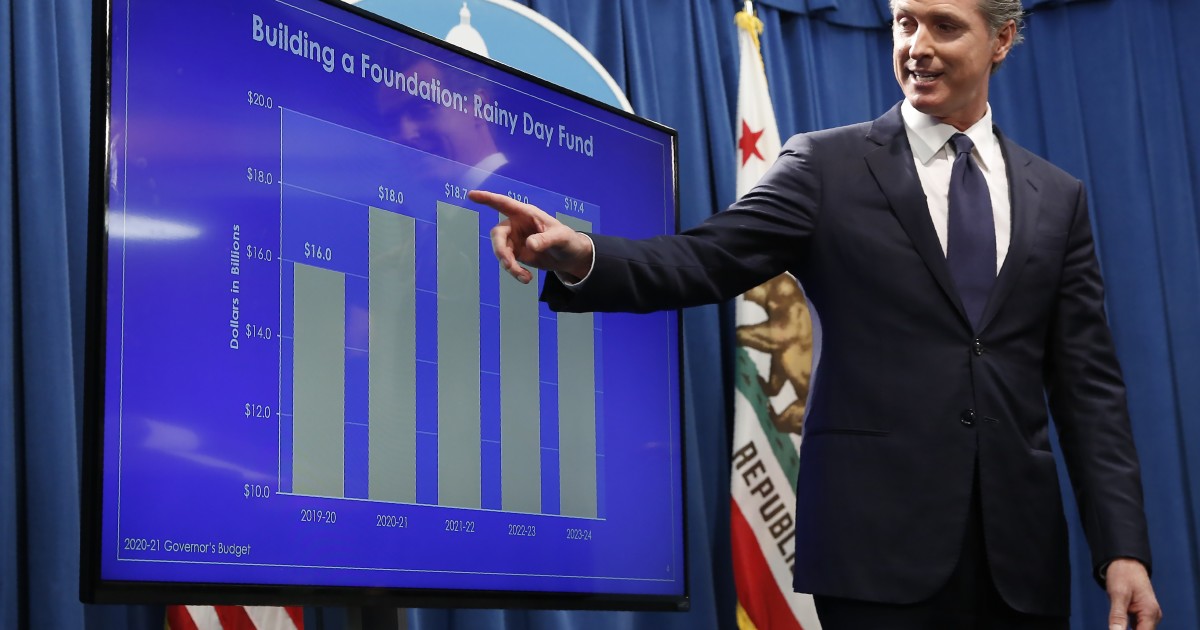
A report from the bipartisan Legislative Analyst’s Office says California’s savings account could grow to more than $18 billion by the end of 2021.
California had a record $21.5 billion surplus in the state budget in 2018. Newsom and the Democratic-controlled state Legislature spent more than half of that money on paying down debts and boosting reserves.
About $4 billion of it went to support ongoing programs while the rest was used for one-time projects. Where did it go exactly and where is it going? Small business owners deserve to know.
As Congress debates more funding, a contentious point was federal dollars bailing out states… we see now that Pelosi is lying as California does not need a bailout.

With a looming recession and possible federal cuts, where will the money go?
By Evan Symon
The California Legislative Analyst’s Office found that the state will have an extra $7 billion that wasn’t spent in the budget. And by 2021 there can be as much as $18 billion in the state’s general fund.
This is a long way away from a decade ago when the state was about that much in the red.
While the number may go down $2 billion if the Trump administration removes the state Medicaid tax, which it has strongly indicated it will do, it still leaves billions of dollars of extra money sitting in California’s coffers. It’s just a matter of deciding what to do with it.
A Rainy Day Fund
The most likely option for state lawmakers would be to save the extra money, put it into a savings account, and let it accumulate money from both interest and additional surpluses until the next major financial crisis.
A recession is likely coming, and a major natural disaster such as an earthquake is always possible. The LAO even made it clear in the report that “This does not necessarily mean a broader economic slowdown is imminent in the near term. Nonetheless, there likely is greater risk in the economic outlook for 2020-21 than in previous budget cycles.”
Nevertheless, an additional $18 billion would get California through a recession with minimal budget cuts. And after what happened to California during the last recession, where the state was cutting back working days of state employees and giving literal IOUs to banks, a rainy day fund would give California a lot of much needed breathing room, not to mention having an advantage over most states.
And with tax revenue expected to level out in the coming years due to a slow down of wage growth, it may be the most percipient option.
Paying Debts
Despite a surplus in the budget, California still has debt. A LOT of debt.
In 2017 it was estimated that California is still in the red somewhere between $26 billion and $1.3 trillion. Much of that comes from state pensions – pensions of which will be draining more soon due to more baby boomers retiring.
This is another popular option, as Governor Newsom spent half of last years surplus of $21.5 billion paying off this debt. While this won’t nearly pay it all off overnight, eating into some of that now could help future debt issues in the future.
Protection against Federal cuts
Currently California is standing to lose $2 billion each year in surplus due to losing the aforementioned state Medicaid tax. If it is lost, the surplus takes care of that lost revenue, right off the bat.
Due to the Trump administration’s dislike of California, and other Federal program cuts that are possible in the upcoming years, a surplus could help fill in the gap of anything taken away. Lawmakers across California have mentioned this being a scenario before, with a federal cut hurting Californians across the board.
“The state is not in this alone,” said Assemblyman Anthony Rendon (D-Lakewood). “Federal actions may hurt our budget in three ways: by damaging the economy as a whole, by hurling fiscal threats at our revenues, and by withholding funds for programs that benefit Californians.”
Like a rainy day fund, this would only be for the worst case scenario. And it’s one where it can’t even be estimated on because of likely shifts in the Presidency, House of Representatives, and Senate next year.
Infrastructure
California currently has about $187 billion in infrastructure needs. Many roads, highways, bridges, rail lines and other transport repairs, upgrades, demolitions, and new constructions are needed across the state. Former Governor Jerry Brown himself had been very adamant about extra money going towards neglected transportation needs.
Like the overall state debt, a few billion a year going to new infrastructure would only put a small dent into what is needed. But with many bridges and other vital facilities possibly failing and causing injury and death if their problems are ignored for too long, infrastructure also makes sense for surplus spending.
A good lesson for the state
A budget surplus is a good problem to have. California has, for now, learned its’ lesson on overspending on immediate budget needs, and has gone from being the butt of national jokes to becoming the budgetary model for the United States.
“President Trump talks a lot about America’s economic growth under his presidency, but when you look behind the numbers, you see it’s California’s growth that has provided the economic rocket fuel for the nation,” Governor Newsom said about the budget surplus. “The federal government would be wise to look to California as a model for how to get its fiscal house in order.”
When it comes to immediate budgeting, California is back on track. How it decides to spend the current surplus would only validate that.
However the surplus is tiny compared to how much California really has in debt, which is well over a trillion dollars when state employee pension and healthcare plans are added in. The Globe will take a look at the other side of the surplus and California’s debt in Part II.