By: Denise Simon | Founders Code
Primer questions: Did other tech companies do the same and if so, how many? What does Congress know and where are they with a real cyber policy?
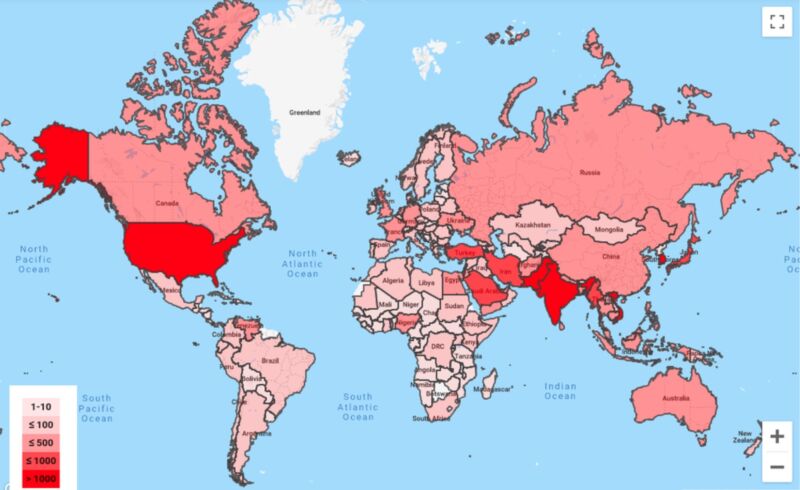
Google’s threat analysis group, which counters targeted and government-backed hacking against the company and its users, sent account holders almost 40,000 warnings in 2019, with government officials, journalists, dissidents, and geopolitical rivals being the most targeted, team members said on Thursday.
The number of warnings declined almost 25 percent from 2018, in part because of new protections designed to curb cyberattacks on Google properties. Attackers have responded by reducing the frequency of their hack attempts and with being more deliberate. The group saw an increase in phishing attacks that impersonated news outlets and journalists. In many of these cases, attackers sought to spread disinformation by attempting to seed false stories with other reporters. Other times, attackers sent several benign messages in hopes of building a rapport with a journalist or foreign policy expert. The attackers, who most frequently came from Iran and North Korea, would later follow up with an email that included a malicious attachment.
“Government-backed attackers regularly target foreign policy experts for their research, access to the organizations they work with, and connections to fellow researchers or policymakers for subsequent attacks,” Toni Gidwani, a security engineering manager in the threat analysis group, wrote in a post.
Top targets
Countries with residents that collectively received more than 1,000 warnings included the United States, India, Pakistan, Japan, and South Korea. Thursday’s post came eight months after Microsoft said it had warned 10,000 customers of nation-sponsored attacks over the 12 previous months. The software maker said it saw “extensive” activity from five specific groups sponsored by Iran, North Korea, and Russia.
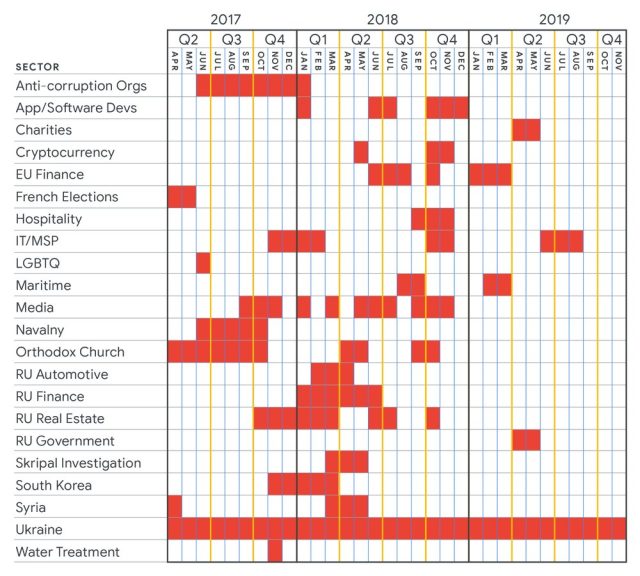
Thursday’s post also tracked targeted attacks carried out by Sandworm, believed to be an attack group working on behalf of the Russian Federation. Sandworm has been responsible for some of the world’s most severe attacks, including hacks on Ukrainian power facilities that left the country without electricity in 2015 and 2016, NATO and the governments of Ukraine and Poland in 2014, and according to Wired journalist Andy Greenberg, the NotPetya malware that created worldwide outages, some that lasted weeks.
The following graph shows Sandworm’s targeting of various industries and countries from 2017 to 2019. While the targeting of most of the industries or countries was sporadic, Ukraine was on the receiving end of attacks throughout the entire three-year period:
Tracking zero-days
In 2019, the Google group discovered zero-day vulnerabilities affecting Android, iOS, Windows, Chrome, and Internet Explorer. A single attack group was responsible for exploiting five of the unpatched security flaws. The attacks were used against Google, Google account holders, and users of other platforms.
“Finding this many zeroday exploits from the same actor in a relatively short time frame is rare,” Gidwani wrote.
The exploits came from legitimate websites that had been hacked, links to malicious websites, and attachments embedded in spear-phishing emails. Most of the targets were in North Korea or were against individuals working on North Korea-related issues.
The group’s policy is to privately inform developers of the affected software and give them seven days to release a fix or publish an advisory. If the companies don’t meet that deadline, Google releases its own advisory.
One observation that Google users should note: of all the phishing attacks the company has seen in the past few years, none has resulted in a takeover of accounts protected by the account protection program, which among other things makes multifactor authentication mandatory. Once people have two physical security keys from Yubi or another manufacturer, enrolling in the program takes less than five minutes.